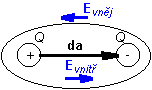
Slovník pojmůElementary electric dipoleAssume an ideal dielectric (no free charges). Positive and negative charges form together neutral atoms (charges can move inside the atom only). If static external electric field takes the effect, then atoms keeps the neutrality in their whole, but the gravity center of positive and negative charges shifts. Atoms are polarized (atoms become electric dipoles).
Electric dipole is described by the moment of electric dipole p [C.m] where da is a positional vector from the negative pole of the atom to the positive one, and Q is charge on poles. If external electric field varies in time, even the magnitude of a charge at the ends of the dipole changes a corresponding way. The changes of the magnitude of charge can be imagined being caused by a current flowing through the dipole (see continuity equation). |